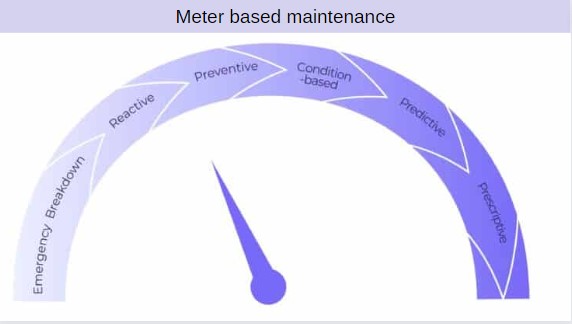
Meter-Based Maintenance Best Practices
Madhurima Sanyal |
15 Jan 2024 |
16:39 PM
- Understanding the Essence of Effective Preventive Maintenance Plans
- Foundations of Maintenance
- Optimization Strategies
- Empowering Your Preventive Maintenance Team
- Addressing Common Queries
- When to Choose for Meter-Based Preventive Maintenance (PM)?
- Conclusion

Optimizing Quality Control: The Role of Inspection Data Management Software
Kirti Prakash 04 Jun 2024 | 14:25 PMDiscover the Most Efficient Inspection Data Management Software for Streamlined Operations....
Unveiling Meter-Based Maintenance Best Practices
Imagine a maintenance strategy that goes beyond the conventional, one that adapts and evolves with the heartbeat of your equipment – that's the essence of Meter-Based Preventive Maintenance. By incorporating data-driven strategies, businesses can revolutionize their maintenance strategy, ensuring not just longevity but optimal functionality of their assets.
In a world where every second counts, uncovering the nuances of Meter-Based Preventive Maintenance becomes imperative. It's not just about fixing issues; it's about preventing them with calculated precision. We'll delve into the key aspects of preventive maintenance strategy, exploring how meter reading become the guiding force for a proactive strategy that prevents costly repairs.
Understanding the Essence of Effective Preventive Maintenance Plans
Effective maintenance is more than just a checklist; it's a strategic approach to safeguarding your investments. In this subsection, we'll unravel the significance of preventive maintenance programs and the role they play in ensuring your assets operate at their peak. We'll explore how implementing preventive maintenance activities can be a game-changer, not only in terms of efficiency but also in mitigating unnecessary downtime and costly repairs.

Through step-by-step guidance and real-world examples, we aim to demystify the concept of meter-based maintenance management, making it accessible and actionable for businesses of all sizes.
Foundations of Maintenance
Exploring Meter-Based Maintenance
Meter-Based Maintenance involves utilizing meter reading to schedule maintenance activities. By consistently monitoring equipment metrics, maintenance technicians can anticipate and address potential issues before they lead to failures. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, reduces repair costs, and ensures assets operate at optimal levels. Businesses benefit from increased equipment reliability and longevity, translating to enhanced operational efficiency.
Diving into Periodic Maintenance

Regular maintenance follows a scheduled approach for equipment upkeep. It involves regularly inspecting, cleaning, and servicing machinery to prevent wear and tear. These management strategies ensures that equipment operates smoothly, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns. By implementing planned maintenance, businesses experience peak performance of assets, lower repair costs, and prolonged asset life.
Decoding Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
Predictive Maintenance (PdM) relies on data analytics and sensor technologies to predict equipment failures before they occur. By analyzing historical data and real-time metrics, businesses can identify patterns and potential issues, enabling timely interventions. PdM minimizes unplanned downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of critical assets. It empowers organizations to shift from reactive to proactive maintenance, optimizing overall operational efficiency.
Optimization Strategies
Automating Meter-Based Maintenance
Automation is the cornerstone of modern preventive maintenance practices. By incorporating automated systems to collect and analyze meter readings, businesses streamline their preventive maintenance processes. This not only reduces the workload on preventive maintenance teams but also ensures accurate and timely data-driven decisions. Automation not only saves time but also minimizes the chances of oversight, paving the way for a more proactive maintenance approach.
Building a Comprehensive Asset Inventory

Effective maintenance begins with a clear understanding of your assets. Building a comprehensive equipment inventory involves cataloging all equipment, noting specifications, and recording maintenance histories. This inventory becomes the foundation for strategic decision-making, helping prioritize maintenance tasks and allocate resources efficiently. By having a detailed asset inventory, businesses gain insights into the health of their equipment, enabling them to tailor meter based preventive maintenance tasks based on actual needs.
Asset Prioritization for Optimal Performance
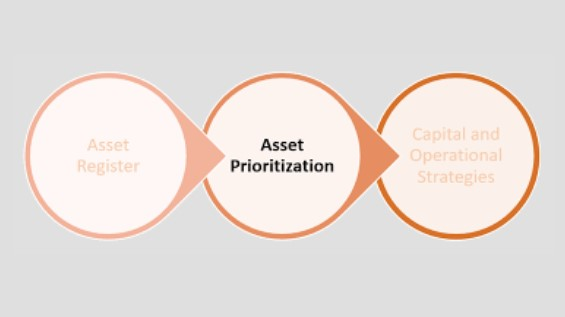
Not all assets are created equal. Asset prioritization is the art of categorizing equipment based on criticality and performance impact. By strategically prioritizing assets, businesses ensure that resources are allocated where they are needed most. This approach minimizes downtime for mission-critical equipment, leading to optimal performance across the board. Imagine a scenario where your maintenance tasks are precisely directed, maximizing the overall efficiency of your operations.
Preventive Maintenance Precision

Crafting a Meter-Driven Preventative Maintenance Schedule
Crafting preventive maintenance strategies are driven by meter readings is a strategic approach that ensures preventive maintenance tasks are precisely timed. By leveraging data from equipment meters, businesses can establish a proactive maintenance routine tailored to the specific needs of each asset. This targeted approach minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns, reduces downtime, and optimizes the lifespan of equipment.
Comparative Analysis: Time-Based vs. Meter-Based PM
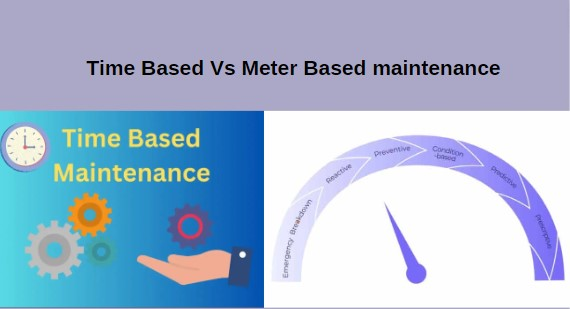
In this section, we undertake a comparative analysis between time-based and meter-based preventive maintenance (PM). Time-based PM relies on predetermined intervals, often resulting in over-maintenance or, conversely, missing critical interventions. On the other hand, meter-based PM is driven by actual usage data, allowing for a more accurate and efficient schedule.
Empowering Your Preventive Maintenance Team
Maximizing Efficiency Through Meter-Based Approaches

Meter-based maintenance approaches are a game-changer for enhancing efficiency. By harnessing real-time data from equipment meter readings, your maintenance managers gain valuable insights into usage based maintenance patterns and performance metrics. This data-driven approach allows for the creation of preventive maintenance program, ensuring interventions are proactive and tailored to prevent equipment downtime.
Navigating Between Time-Based and Meter-Based PM
Navigating between time-based and meter-based preventive maintenance PMS requires a strategic understanding of their strengths and weaknesses. While time-based PM relies on predetermined intervals, meter-based PMS adapts to the actual usage patterns of equipment.
Addressing Common Queries
When to Employ Time-Based Preventive Maintenance (PM)?
 Time-Based Preventive Maintenance program is employed when scheduled interventions are necessary for maintaining equipment and preventing potential issues. This approach is typically based on predetermined time intervals, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or annually, depending on the nature of the equipment and manufacturer recommendations.
Time-Based Preventive Maintenance program is employed when scheduled interventions are necessary for maintaining equipment and preventing potential issues. This approach is typically based on predetermined time intervals, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or annually, depending on the nature of the equipment and manufacturer recommendations.
Time-based PM is particularly suitable for assets that exhibit consistent and predictable patterns of wear and tear, allowing organizations to proactively address maintenance needs before problems arise. Industries with regulatory requirements or specific compliance standards often rely on time-based PM to ensure that equipment remains in compliance with safety and operational guidelines.
When to Choose for Meter-Based Preventive Maintenance (PM)?
Meter-Based Preventive Maintenance (PM) is chosen when maintenance interventions are scheduled based on the actual usage or running time of equipment. This approach relies on continuous monitoring of relevant metrics, such as running hours, cycles, or other usage based maintenance data. Organizations opt for Meter-Based PMS when they seek a proactive strategy that addresses maintenance needs in response to real-time operational conditions.
This method is particularly effective for assets with varying patterns of usage, allowing for a more customized and data-driven approach to maintenance. Industries that operate machinery continuously often favor Meter-Based PMS to optimize the lifespan of equipment and minimize unexpected breakdowns. By analyzing usage based maintenance data, organizations can determine optimal maintenance intervals, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Adopting meter-based maintenance practices emerges as a strategic imperative for businesses seeking precision and efficiency in asset management. By demystifying the intricacies of time-based versus meter-based approaches, empowering maintenance teams with optimized strategies, and addressing common queries, organizations can maximize operational efficiency. The insights provided in this guide offer a comprehensive understanding of the nuanced world of maintenance.
As industries evolve, embracing meter-driven approaches becomes pivotal, ensuring not only prolonged asset life but also fostering a culture of proactive and data-informed decision-making. Elevate your maintenance game, unlock potential savings, and propel your business towards sustained success.