Asset Lifecycle Management - Best Practices
Madhurima Sanyal |
21 Feb 2024 |
12:40 PM
- What is an asset?
- Understanding Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM)
- Importance of Efficient Asset Lifecycle Management
- Asset Lifecycle Stages
- Implementing Best Practices for Asset Lifecycle Management
- Benefits of Asset Lifecycle Management
- Crafting an Effective Asset Lifecycle Management Strategy
- Conclusion

5 reasons why businesses should implement EAM software
Pratik Lohiya 05 Jan 2024 | 18:13 PMDiscover the transformative power of Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) systems in our comprehensive blog. Learn how EAM software enhances efficiency, reduces costs, ensures compliance, and drives strategic decision-making for businesses across industr...
Introduction to Asset Lifecycle Management
In business, assets can range from physical equipment and machinery to intellectual property and software licenses. Understanding Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM) involves recognizing the journey an asset takes from acquisition to disposal. It encompasses planning, procurement, utilization, and disposal stages. Efficient Asset Lifecycle Management ensures optimal utilization, cost-effectiveness, and regulatory compliance throughout an asset's lifespan.
What is an asset?
An asset is any valuable resource owned by an individual or organization that contributes to their financial well-being. These can encompass physical assets like machinery, equipment, and property, as well as intangible assets such as patents, trademarks, and software licenses. Understanding the diverse nature of assets is crucial for effective management and strategic decision-making within any business or entity.
Understanding Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM)

Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM) refers to the systematic approach of managing an asset throughout its entire lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal. It involves strategic planning, procurement, utilization, maintenance, and ultimately, decommissioning. ALM ensures that assets are utilized optimally, maintained effectively, and replaced or disposed of responsibly when necessary. By comprehensively managing assets throughout their lifecycle, organizations can maximize their value, minimize risks, and enhance operational efficiency.
Importance of Efficient Asset Lifecycle Management
Efficient Asset Lifecycle Management is crucial for organizations to achieve their strategic objectives and maintain a competitive edge in today's dynamic business environment. It ensures that assets are utilized effectively, maintained proactively, and replaced or upgraded in a timely manner to meet evolving needs. Effective ALM also facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements, reduces operational costs, and enhances overall productivity and profitability. By adopting best practices in asset lifecycle management, organizations can optimize asset performance, mitigate risks, and drive sustainable growth in the long run.
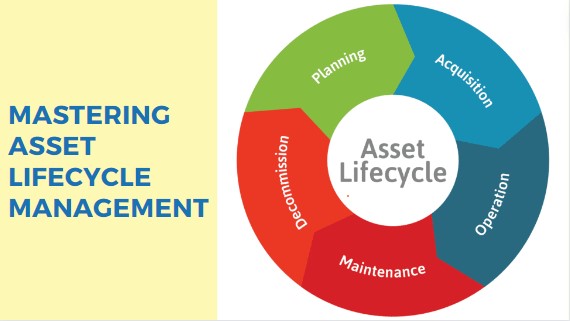
Asset Lifecycle Stages
Acquisition and Planning
During this initial stage, organizations identify their asset needs, conduct feasibility studies, and develop acquisition plans. This involves assessing budgetary constraints, regulatory requirements, and operational needs to ensure the right assets are acquired at the right time.
Installation and Commissioning
Assets are installed, configured, and integrated into existing systems during this stage. Commissioning involves testing and verifying that assets function according to specifications and meet performance standards.
Operation and Maintenance
Assets are utilized in daily operations and undergo regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Preventive maintenance strategies are implemented to mitigate potential breakdowns and takes care of asset life cycle management processes.

Upgrades and Modifications
As technology evolves or business needs change, assets may require upgrades or modifications to remain relevant and efficient. This stage involves assessing upgrade options, implementing necessary changes, and ensuring seamless integration with existing systems.
Decommissioning and Disposal
At the end of their useful life, assets are decommissioned and disposed of responsibly. This includes safely removing assets from operation, documenting their disposal, and adhering to environmental regulations to minimize impact. Proper disposal ensures compliance and frees up resources for new investments.
Implementing Best Practices for Asset Lifecycle Management
Utilizing Asset Lifecycle Management Software
Implementing advanced asset lifecycle management software allows organizations to streamline processes, centralize asset data, and enhance decision-making throughout the asset life cycle, ensuring efficient utilization and maintenance.
Integrating Preventive Maintenance
By integrating preventive maintenance schedules based on asset usage data, organizations can proactively identify and address potential issues, minimizing costly breakdowns, and extending physical asset's life while optimizing operational efficiency.
Reducing Emergency Repairs

Implementing preventive maintenance measures helps minimize unplanned downtime and reduces the need for costly emergency repairs, enhancing overall asset life cycle and decreasing operational disruptions.
Specifying Asset Roles in Operations
Clearly defining asset roles and responsibilities ensures efficient utilization, maintenance, and tracking throughout their lifecycle, enhancing accountability and optimizing asset performance.
Extending Asset Life and Reducing Downtime
Regular maintenance, timely upgrades, and strategic asset management practices help extend asset life and minimize downtime, ensuring continuous productivity and optimizing asset life cycle management.
Real-time Data Analysis for Performance Optimization
Utilizing real-time data analytics enables organizations to identify performance trends, predict maintenance needs, and optimize asset utilization for maximum efficiency, leading to improved decision-making and cost savings.
Implementing Asset Tracking Systems
Asset tracking systems provide real-time visibility into asset location, condition, and usage, enabling proactive management and minimizing loss or theft, thus ensuring operational continuity of asset's life cycle.
Budgeting for Asset Maintenance
Allocating sufficient resources for asset maintenance ensures timely repairs, upgrades, and replacements, optimizing asset performance and ROI over time, while also minimizing the risk of unexpected costs and disruptions.
Benefits of Asset Lifecycle Management
Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM) offers numerous benefits to organizations across various industries, allowing them to optimize asset utilization, minimize costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Here are some key advantages:
Maximizing Asset Performance and Efficiency
ALM enables organizations to maximize the performance and efficiency of their assets throughout their entire lifecycle. By implementing best practices such as preventive maintenance, timely upgrades, and strategic planning, organizations can ensure that assets operate at peak performance levels, resulting in increased productivity and profitability.
Optimizing Asset Utilization
Effective asset life cycle management ensures that assets are utilized optimally throughout their lifecycle. By closely monitoring asset usage and performance data, organizations can identify underutilized assets, reallocate resources, and make informed decisions about asset acquisition and deployment, ultimately maximizing the return on investment (ROI) for each asset.
Minimizing Downtime and Disruptions
Good asset management strategy helps organizations minimize downtime and disruptions by proactively managing asset maintenance and repair activities. By implementing preventive maintenance strategies and utilizing real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, organizations can identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns, ensuring continuous operations and customer satisfaction.
Enhancing Regulatory Compliance
ALM assists organizations in maintaining regulatory compliance by ensuring that assets meet relevant safety, environmental, and industry-specific standards throughout their lifecycle. By maintaining accurate records, implementing proper maintenance procedures, and conducting regular audits, organizations can mitigate compliance risks and avoid high maintenance costs.
Improving Decision-Making
ALM provides organizations with valuable insights and data-driven intelligence that can inform strategic decision-making processes. By analyzing asset performance metrics, lifecycle costs, and risk factors, organizations can make informed decisions about asset investments, upgrades, and replacements, optimizing resource allocation and driving long-term business success.
Crafting an Effective Asset Lifecycle Management Strategy
Understanding Enterprise Asset Management Systems (EAMs)
Enterprise Asset Management Systems (EAMs) are comprehensive asset management software solutions designed to streamline and optimize the management of an organization's critical and physical assets throughout their entire lifecycle. These systems facilitate efficient planning, procurement, utilization, maintenance, and disposal of assets.
EAMs provide centralized repositories for asset data, enabling organizations to track asset performance, monitor maintenance schedules, and manage asset-related costs effectively. By integrating various modules such as maintenance management, inventory control, and financial management, EAMs enable organizations to make data-driven decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and maximize the value of their assets.
Utilizing Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) are software tools specifically designed to facilitate and streamline maintenance operations. CMMS software enables organizations to schedule preventive maintenance tasks, track work orders, manage inventory, and generate reports for analysis.
By digitizing maintenance processes, CMMS helps organizations reduce downtime, optimize maintenance schedules, and extend asset lifespan. These systems also enable better resource allocation, enhance asset reliability, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Implementing Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Preventive maintenance strategies involve proactively scheduling maintenance tasks based on predetermined criteria such as time, usage, or performance indicators. By conducting regular inspections, servicing, and repairs, organizations can identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns.
Proactive maintenance strategies help extend asset lifespan, minimize downtime, and optimize operational efficiency. These strategies also contribute to improved safety, compliance with regulatory requirements, and enhanced asset reliability, ultimately leading to increased productivity and reduced maintenance costs.
Importance of Asset Tracking in Lifecycle Management
Asset tracking plays a crucial role in lifecycle management by providing real-time visibility into asset location, status, and usage. By utilizing asset tracking solutions, organizations can accurately monitor asset movements, track maintenance activities, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Asset tracking enables proactive decision-making, facilitates timely maintenance interventions, and minimizes the risk of asset loss or theft. Additionally, asset tracking data can inform strategic asset management decisions, optimize asset utilization, and ultimately enhance organizational efficiency and profitability.
Conclusion
Effective management of assets throughout their lifecycle is essential for organizations to achieve operational excellence, maximize returns on investments, and maintain a competitive edge in today's dynamic business environment. Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM) encompasses strategic planning, procurement, utilization, maintenance, and disposal of assets, ensuring their optimal performance and longevity.
By implementing best practices and leveraging advanced technologies, such as asset management software solutions, organizations can streamline processes, centralize asset data, and improve decision-making. Integrating preventive maintenance strategies, monitoring asset performance, and utilizing real-time data analytics enable organizations to minimize downtime, reduce costs, and enhance asset's life cycle.
Furthermore, asset tracking systems provide visibility into asset information, location, condition, and usage, enabling proactive management and minimizing risks associated with critical assets. Effective asset management strategies also contribute to regulatory compliance, improve resource allocation, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
In essence, embracing asset lifecycle management best practices empowers organizations to optimize asset utilization, minimize risks, and drive sustainable growth. By continuously evaluating and improving asset management processes, organizations can adapt to evolving market conditions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on new opportunities, ultimately ensuring long-term success and prosperity.