
How Optimized Work Orders Increase Productivity
Pratik Lohiya |
13 Mar 2024 |
17:10 PM
- Understanding the Importance of Efficient Work Order Management
- What is Work Order Management?
- The Work Order Lifecycle
- Work Order Planning and Scheduling
- Leveraging Technology: CMMS for Work Order Management
- Best Practices for Work Order Management systems
- Industries and Applications
- Industries that Benefit from Work Order Management process
- Maintenance Work Orders
- How To Create an Effective Maintenance Work Order
- Conclusion

Comprehensive Guide to Work Order Management Process
Pratik Lohiya 17 May 2024 | 07:15 AMIn this comprehensive guide, explore the complexities of the Work order management process, its significance, maintaining operational harmony, best practices and KPIs. Get started today! ...
Efficient work order management is the backbone of any successful organization, ensuring smooth operations, timely completion of tasks, and optimal resource utilization. In today's fast-paced business environment, where every minute counts, having an effective work order management system in place is imperative for achieving operational excellence.
Understanding the Importance of Efficient Work Order Management
Efficient work order management goes beyond just assigning tasks to employees. It encompasses a structured approach to planning, scheduling, executing, and monitoring work orders to ensure they are completed efficiently and on time. By streamlining the work order process, organizations can minimize downtime, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity.
What is Work Order Management?
Work order management refers to the systematic process of creating, prioritizing, assigning, tracking, and completing tasks within an organization. It involves the coordination of various resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials, to fulfill work orders in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Traditional Work Order Management Process
Traditionally, work order management relied heavily on manual processes, such as paper-based forms and spreadsheets. This approach was time-consuming, prone to errors, and lacked real-time visibility into work order status. Organizations struggled to keep up with the demands of a dynamic work environment, often leading to inefficiencies and delays.
However, with advancements in technology, modern work order management systems have revolutionized the way organizations handle their operations. These systems leverage automation, integration, and data-driven insights to streamline the entire work order process, from initiation to completion.
The Work Order Lifecycle
Overview of the Work Order Lifecycle
The work order lifecycle typically consists of several key stages, starting from the moment a work request is submitted until the task is successfully completed and evaluated. Understanding each stage is essential for organizations to effectively manage their work orders and maintain operational efficiency.
Submitting a Work Request: Key Steps and Considerations
The work order process often begins with the submission of a work request by a customer, employee, or department within the organization. This step involves providing detailed information about the nature of the task, including its priority, location, and any relevant specifications. Effective communication and clear documentation are critical during this stage to ensure that work requests are accurately captured and prioritized.
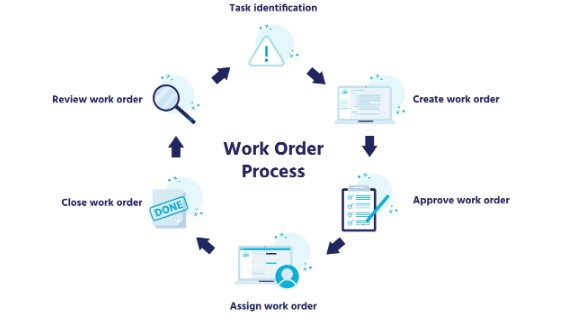
Creating the Work Order - Once a work request is received, it is converted into a formal work order within the work order management system. This involves assigning the task to the appropriate personnel, scheduling it based on priority and resource availability, and providing any necessary instructions or specifications. Utilizing management software can streamline this process, ensuring that work orders are created efficiently and accurately.
Carrying Out the Task - With the work order in hand, technicians or employees can begin executing the assigned task. This stage involves utilizing the allocated resources effectively, adhering to safety protocols, and completing the work according to established standards and timelines. Effective task prioritization and resource allocation are essential for maximizing productivity and minimizing delays.
Completing the Work Order - Once the task is completed, the work order is updated with relevant information, such as the date and time of completion, any materials used, and any issues encountered during the process. This step ensures that all work orders are properly documented and closed out, providing valuable data for future analysis and improvement.
Reviewing the Process - After the work order is completed, it is essential to review the entire process to identify any areas for improvement. This may involve analyzing key performance indicators, soliciting feedback from customers or employees, and implementing changes to optimize the work order management system further. Continuous improvement is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and meeting customer expectations.
Work Order Planning and Scheduling
Effective planning and scheduling are essential components of efficient work order management. By carefully strategizing the allocation of resources and prioritizing tasks, organizations can optimize maintenance efficiency and enhance overall operational performance.
The Work Order Planning Process
The work order planning process begins with identifying maintenance needs and determining the scope of work required. This involves assessing equipment conditions, scheduling routine inspections, and anticipating potential issues to be addressed proactively. Asset management systems play a crucial role in this stage by providing real-time insights into asset health and performance.
Optimizing Maintenance Efficiency: Work Order Planning and Scheduling

Once maintenance needs are identified, the next step is to schedule work orders effectively. This includes prioritizing tasks based on criticality, resource availability, and operational impact. By leveraging data-driven decision-making and management software, organizations can streamline the scheduling process and ensure timely completion of work orders. Continuous improvement efforts further enhance efficiency and enable organizations to optimize their work order management practices for maximum effectiveness.
Scheduling Work Orders
-
Decide on a Scheduling System - Choosing the right scheduling system is crucial for optimizing work order management. Whether it's a manual scheduling process or utilizing advanced scheduling software, organizations must select a system that aligns with their operational needs and objectives. Asset management systems integrated with scheduling capabilities can provide real-time visibility into resource availability and streamline the scheduling process.
-
Decide on Priorities - Prioritizing work orders based on their urgency and impact on operations is essential for effective scheduling. By identifying critical tasks and allocating resources accordingly, organizations can minimize downtime, prioritize customer needs, and maintain high levels of operational efficiency.
-
Determine Ideal Intervals - Determining the ideal intervals for scheduling recurring work orders helps organizations proactively address maintenance needs and prevent potential issues. By establishing regular maintenance schedules based on asset performance data and industry best practices, organizations can minimize downtime and extend asset lifespan.
-
Schedule Recurring Work Orders - Scheduling recurring work orders for routine maintenance tasks is essential for ensuring equipment reliability and performance. By automating the scheduling of preventive maintenance activities, organizations can reduce the risk of unplanned downtime, optimize asset performance, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Utilizing management software with built-in scheduling features can simplify the process of scheduling recurring work orders and ensure they are completed on time.
Leveraging Technology: CMMS for Work Order Management
Today, organizations are increasingly turning to Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) to streamline their work order management processes. CMMS software offers a comprehensive solution for managing work orders, assets, and maintenance activities efficiently.

What is Work Order Management Software?
Work order management software, often integrated within CMMS platforms, is designed to automate and streamline the entire work order lifecycle. It enables organizations to create, assign, track, and manage work orders digitally, replacing traditional paper-based methods with an intuitive and centralized system.
Benefits of Work Order Management Software
-
Operational Efficiency: Work order management software enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and minimizing downtime through proactive maintenance scheduling.
-
Data-Driven Decision Making: By capturing and analyzing data related to work orders, assets, and maintenance activities, organizations can make informed decisions to improve productivity and asset performance.
-
Seamless Communication: Work order management software facilitates seamless communication between stakeholders, enabling real-time collaboration and updates on work order status.
-
Continuous Improvement: With built-in reporting and analytics capabilities, work order management software enables organizations to identify trends, track progress, and implement continuous improvement initiatives for optimized performance.
Leveraging a CMMS to Manage Your Work Orders - Utilizing a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can revolutionize the way organizations manage their work orders. By leveraging the advanced features and capabilities of a CMMS, organizations can streamline their maintenance operations and improve overall efficiency.
-
Automate Work Requests - One of the key benefits of using a CMMS is the ability to automate work requests. Instead of relying on manual processes or paper-based forms, employees can submit work requests directly through the CMMS platform. This not only saves time but also ensures that all relevant information is captured accurately, leading to faster response times and improved customer satisfaction.
-
Monitor Your Work Order Lifecycle - A CMMS enables organizations to monitor the entire lifecycle of their work orders in real-time. From creation to completion, organizations can track the progress of each work order, identify bottlenecks or delays, and take proactive measures to ensure timely completion. This level of visibility and control is essential for optimizing resource allocation, improving operational efficiency, and meeting customer expectations.
Best Practices for Work Order Management systems
Implementing effective best practices for work order management systems is essential for maximizing operational efficiency, minimizing downtime, and ensuring customer satisfaction. By adhering to these practices, organizations can streamline their maintenance operations and optimize resource utilization.
Standardize Work Order Formats
Standardizing work order formats ensures consistency and clarity across all work orders. By establishing a uniform structure for capturing essential information such as task description, priority level, and required resources, organizations can streamline communication and reduce the likelihood of errors or misunderstandings.
Prioritize and Monitor Work Orders
Prioritizing work orders based on urgency, criticality, and impact on operations is crucial for effective resource allocation. Organizations should establish clear criteria for prioritization and regularly monitor work orders to ensure that high-priority tasks are addressed promptly. This helps minimize downtime and ensures that critical assets remain operational.
Assign Work Orders to the Right Technician
Assigning work orders to technicians with the appropriate skills and expertise is essential for efficient execution. By matching tasks to technicians based on their qualifications and availability, organizations can improve productivity and reduce the risk of errors or delays. Asset management systems integrated with work order management software can facilitate this process by providing insights into technician capabilities and workload.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is key to optimizing work order management systems. Organizations should regularly evaluate their processes, identify areas for enhancement, and implement changes to drive efficiency and effectiveness. This may involve leveraging data-driven insights, soliciting feedback from stakeholders, and implementing best practices from industry leaders.
Implementing a CMMS Solution
Implementing a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a fundamental best practice for modern work order management. CMMS software centralizes work order management, automates repetitive tasks, and provides real-time visibility into maintenance activities. By implementing a CMMS solution, organizations can improve coordination, streamline workflows, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Industries and Applications

Work order management processes are essential across various industries and applications, playing a pivotal role in enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and ensuring smooth operations. Let's explore some industries that particularly benefit from efficient work order management processes:
Industries that Benefit from Work Order Management process
Manufacturing: In manufacturing industries, work order management is crucial for scheduling maintenance tasks, tracking equipment downtime, and optimizing production schedules. Preventive maintenance ensures machinery remains operational, minimizing disruptions and maximizing productivity.
Facilities Management: Facilities management relies heavily on work order management to coordinate maintenance activities, manage service requests, and ensure the proper functioning of buildings and infrastructure. Timely response to work orders helps maintain a safe and comfortable environment for occupants.
Healthcare: In healthcare settings, work order management ensures medical equipment is properly maintained, facilities are clean and functional, and patient care is not compromised. Preventive maintenance schedules help prevent equipment failures and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Utilities: Utility companies rely on work order management to maintain critical infrastructure, such as power plants, water treatment facilities, and telecommunications networks. Timely maintenance reduces downtime and ensures uninterrupted service to customers.
Field Service Management: Industries with field service operations, such as telecommunications, HVAC, and construction, benefit from work order management to dispatch technicians, track progress, and deliver services efficiently to customers on-site.
Maintenance Work Orders
Challenges in Maintenance Work Order Management
Lack of Standardization: Without standardized work order formats and processes, organizations may struggle with inconsistency and confusion, leading to errors and delays in task execution.
Manual Data Entry: Relying on manual data entry for creating and updating work orders increases the risk of errors and can be time-consuming. It also hinders real-time visibility into work order status and progress.
Communication Barriers: Inadequate communication channels between departments, technicians, and stakeholders can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and inefficiencies in work order management.
Resource Allocation: Allocating resources effectively to address maintenance needs while balancing other operational demands can be challenging. Poor resource allocation may result in delays or insufficient support for critical tasks.
How To Create an Effective Maintenance Work Order
Standardize Work Order Formats: Establish standardized templates for creating work orders, including essential details such as task description, priority level, required materials, and completion criteria. This ensures clarity and consistency across all work orders.
Utilize Management Software: Implementing maintenance management software streamlines work order creation, tracking, and reporting processes. Automated workflows reduce reliance on manual data entry, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Facilitate Clear Communication Channels: Implement communication tools and protocols to ensure seamless collaboration between departments and stakeholders. Clear communication channels enable timely updates, feedback, and resolution of issues.
Embrace Preventive Maintenance: Incorporate preventive maintenance schedules into work orders to proactively address equipment maintenance needs and minimize downtime. This helps prolong asset lifespan and prevents costly repairs.

Monitor Progress and Make Necessary Adjustments: Continuously monitor work order progress, track completion times, and analyze performance metrics to identify areas for improvement. Make necessary adjustments to optimize resource allocation and enhance productivity.
Improving Productivity at Every Stage: Achieving productivity at every stage of the work order management process is essential for maximizing efficiency and delivering exceptional results. By customizing and optimizing each stage, organizations can gain complete control over their operations and enhance productivity across the board.
Customize and Optimize for Complete Control: Customizing work order processes is essential for organizations to tailor their management systems to meet specific needs and achieve optimal results. By customizing workflows, forms, and procedures, companies can streamline operations, eliminate unnecessary steps, and ensure efficient handling of work orders from initiation to completion.
Effective resource allocation is equally crucial in maximizing productivity and minimizing waste. Leveraging management software provides valuable insights into resource availability, workload distribution, and task prioritization, enabling organizations to allocate resources effectively and ensure timely completion of tasks within budget constraints. Clear communication channels are vital for fostering collaboration and ensuring alignment among stakeholders. Implementing communication tools and protocols facilitates seamless interaction between departments, technicians, and stakeholders, reducing delays and misunderstandings.
Empowering the mobile workforce with access to work order management software on their devices enhances productivity by enabling real-time updates, remote access to work orders, and on-the-go task completion. Furthermore, analyzing data-driven insights facilitates continuous improvement by identifying areas for enhancement and informing informed decision-making. By customizing, optimizing, and leveraging technological solutions, organizations can achieve complete control over their operations, streamline processes, minimize errors, and deliver exceptional results consistently.
Conclusion
An effective work order management is paramount for organizations striving to optimize productivity, enhance efficiency, and deliver superior results. By customizing and optimizing work order processes, companies can tailor their management systems to meet specific needs, streamline operations, and ensure efficient handling of tasks. Leveraging management software provides valuable insights into resource allocation, workload distribution, and task prioritization, enabling organizations to allocate resources effectively and ensure timely task completion.
Clear communication channels foster collaboration and alignment among stakeholders, reducing delays and misunderstandings. Empowering the mobile workforce with access to work order management software enhances productivity by facilitating real-time updates, remote access to work orders, and on-the-go task completion. Additionally, analyzing data-driven insights enables continuous improvement by identifying areas for enhancement and informing informed decision-making.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can achieve complete control over their operations, streamline processes, minimize errors, and consistently deliver exceptional results. Moving forward, it is imperative for organizations to prioritize the optimization of work order management processes and embrace technological advancements to stay competitive in today's dynamic business landscape. With a commitment to continuous improvement and innovation, organizations can adapt to evolving challenges and thrive in an ever-changing environment.