
Top 5 Work Order Management Best Practices
Madhurima Sanyal |
23 Jan 2024 |
18:12 PM
- What is a work order?
- Understanding the importance of effective Work Order Management
- Benefits of Work Order Management Processes
- Understanding Work Order Management Software
- What is work order management software?
- Benefits of work order software
- Work Order Basics
- Types of work orders
- Work order versus work request
- What should a work order include?
- Work Order Management Process
- Finalizing Documentation
- Completing Review and Analysis
- Top 5 Work Order Management Best Practices
- Conclusion
.jpg)
What is a work order? 5 steps for the perfect work order
Pratik Lohiya 09 Jan 2024 | 13:51 PMOptimize maintenance efficiency with powerful work order management software. Streamline tasks, boost productivity, and ensure seamless facility operations. Get started on a work order management software today....
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Work Order Management, where we explore essential practices that can elevate your organizational efficiency. In today's dynamic business environment, effective Work Order Management is pivotal for streamlined operations and optimal resource utilization.
What is a work order?
A Work Order serves as a structured directive that outlines the tasks, timelines, and resources required to complete a specific job or maintenance task. It serves as a crucial document, bridging the communication gap between different stakeholders within an organization. Work Orders range from routine maintenance assignments to urgent repairs, playing a key role in maintenance operations and safety of facilities.
Understanding the importance of effective Work Order Management
The importance of effective Work Order Management cannot be overstated. It is the linchpin that ensures tasks are executed systematically, minimizing downtime and preventing potential issues. By establishing standardized processes and protocols, organizations can enhance communication, optimize resource allocation, and proactively address maintenance needs.

Efficient Work Order Management contributes to cost savings by preventing unnecessary repairs and ensuring timely maintenance. It empowers organizations to prioritize tasks based on urgency, allocate the right maintenance technicians, and maintain a comprehensive record of all maintenance activities.
Benefits of Work Order Management Processes
Implementing a robust Work Order Management system comes with a myriad of benefits. It enables organizations to:
-
Prioritize and Monitor Work Orders: By categorizing work orders based on priority, organizations can ensure that critical tasks receive immediate attention, minimizing the risk of equipment failure.
-
Optimize Resource Allocation: Work Order Management allows for the strategic assignment of tasks to the right technicians, ensuring that individuals with the appropriate skills and expertise handle each job.
-
Enhance Preventive Maintenance: A well-organized system facilitates the implementation of preventive maintenance practices, reducing the likelihood of equipment breakdowns and prolonging asset life.
-
Facilitate Data-Driven Decision-Making: Work Order Management systems generate valuable data and insights, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, identify trends, and continuously improve operational processes.

Understanding Work Order Management Software
In the contemporary landscape of facilities and maintenance management, Work Order Management Software stands as a technological cornerstone, transforming the way organizations handle and streamline their operations. Let's learn what Work Order Management Software truly encompasses and the host of benefits it brings to the table.
What is work order management software?
Work Order Management Software is a digital solution designed to automate and optimize the entire work order lifecycle. It serves as a centralized platform that allows organizations to create, assign, track, and analyze work orders seamlessly. This software is engineered to enhance collaboration among various departments, ensuring a cohesive approach to maintenance and task management.

Work Order Management Software is equipped with features such as task prioritization, real-time tracking, and reporting capabilities. It replaces traditional paper-based systems, offering a more efficient and transparent way to handle work orders. This technology is scalable, catering to the needs of both small businesses and large enterprises.
Benefits of work order software
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Work Order Management Software automates routine tasks, reducing manual effort and minimizing the chances of errors. This efficiency boost translates to quicker response times and increased overall productivity.

Streamlined Communication: Communication breakdowns are a common challenge in maintenance operations. Work Order Software ensures seamless communication by providing a centralized platform for all stakeholders to collaborate. Maintenance , managers, and requesters can easily communicate and share updates in real-time.
Data-Driven Decision Making: The software generates comprehensive reports and analytics, offering valuable insights into maintenance trends, asset performance, and workforce efficiency. This data empowers organizations to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and allocate resources effectively.
Improved Asset Management: It facilitates better control and visibility over assets. Organizations can track the maintenance history of each asset, schedule preventive maintenance, and ensure that equipment operates at peak performance.
Faster Response to Urgent Requests: In industries where timely response is critical, such as healthcare or manufacturing, Work Order Software ensures that urgent requests are swiftly addressed. Priority-based scheduling allows organizations to allocate resources efficiently, minimizing downtime.

Cost Savings: By preventing equipment breakdowns through proactive maintenance and optimizing resource allocation, Work Order Software contributes to significant cost savings over time.
Work Order Basics
Work orders serve as the backbone of effective maintenance and operational workflows. Understanding the basics of work orders, the various types, and distinguishing them from work requests is crucial for fostering an organized and efficient work environment.
Types of work orders

Work orders come in different forms, each tailored to address specific maintenance needs. Here are some common types:
-
Preventive Maintenance Work Orders: These work orders involve scheduled tasks to prevent equipment breakdowns and ensure the ongoing reliability of assets.
-
Corrective Maintenance Work Orders: Issued in response to unexpected breakdowns or malfunctions, corrective maintenance work orders aim to restore equipment to optimal functionality.
-
Emergency Maintenance Work Orders: Critical issues requiring immediate attention, such as equipment failures posing safety risks, fall under emergency maintenance work orders.

-
Predictive Maintenance Work Orders: Leveraging data and analytics, predictive maintenance work orders aim to address potential issues before they escalate, based on equipment performance patterns.
Work order versus work request
While work orders and work requests are closely related, they serve distinct purposes in the maintenance process.
-
Work Request: A work request is an initial notification from a requester about a potential issue or need for maintenance. These maintenance requests acts as a precursor to a work order, outlining the problem and requesting attention.
-
Work Order: A work order, on the other hand, is a formal document that details the tasks, resources, and timelines required to address a specific maintenance issue. It is generated based on maintenance requests or as part of a planned maintenance process.
What should a work order include?
A well-crafted work order management process serves as a comprehensive guide for maintenance managers and maintenance department. It typically includes:
-
Detailed Description of the Task: Clearly outline the nature of the maintenance or repair task to provide technicians with a thorough understanding of the job.
-
Assigned Personnel: Specify the maintenance technician responsible for executing the work order to ensure accountability.
-
Timeline and Priority: Establish a timeline for task completion and prioritize work orders based on urgency to optimize resource allocation.
-
Required Materials and Resources: List the materials, tools, and equipment needed to execute the task successfully, preventing delays due to unpreparedness.
-
Equipment Information: Include relevant details about the equipment or asset requiring maintenance, such as model, serial number, and location.
Understanding these work order basics lays the foundation for effective maintenance management. In the subsequent sections, we will explore best practices for creating, managing, and optimizing maintenance processes.
Work Order Management Process
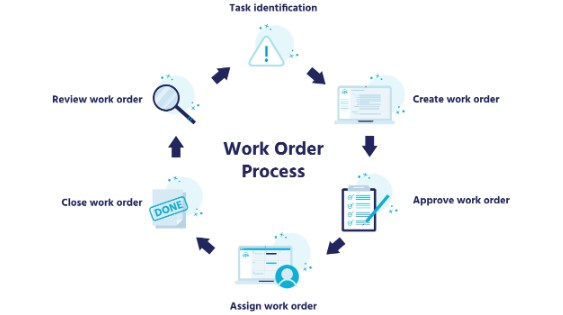
The Work Order Management process is a structured and intricate journey that organizations navigate to ensure efficient handling of maintenance tasks. Let's explore the comprehensive lifecycle of a work order, from the initial request to the final analysis.
The lifecycle of a work order
-
Submitting a Work Request: The process begins when a stakeholder identifies a maintenance need and submits a work request. This initial step sets the stage for assessing the nature of the task and determining its priority.
-
Evaluating a Work Request: Work requests undergo a thorough evaluation to determine their validity and urgency. This involves assessing factors such as the impact on operations, safety concerns, and the overall importance of the maintenance task.
-
Creating a Work Order: Upon approval of a work request, a formal work order is created. This document includes detailed information about the task, such as the nature of the maintenance required, designated personnel, and a timeline for completion.
-
Assigning a Work Order: The next step is the assignment of the work order to the appropriate personnel or maintenance team. This involves considering the skills and expertise required for the task and ensuring that the assigned technician are adequately equipped to address the issue.
-
Performing Maintenance and Closing Out the Work Order: With the work order assigned, maintenance teams execute the necessary maintenance tasks. This phase involves performing the necessary repairs, replacements, or inspections outlined in the work order. Upon completion, the work order is closed out, signifying the successful resolution of the maintenance task.
Finalizing Documentation
Once a work order is closed, the documentation process begins. Finalizing documentation is a critical aspect of the Work Order process for several reasons:
-
Record Keeping: Comprehensive documentation ensures a detailed record of all completed work orders, providing a historical reference for future maintenance needs and audits.
-
Performance Analysis: The data collected from finalized work orders facilitates performance analysis. Organizations can assess completion times, identify recurring issues, and measure the overall efficiency of their maintenance team.
-
Compliance and Audits: Well-documented work orders contribute to regulatory compliance and audits. Having a transparent record of maintenance activities helps organizations demonstrate adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Completing Review and Analysis
Post-maintenance, it's crucial to conduct a thorough review and analysis of the completed work orders. This involves:
-
Performance Evaluation: Assessing the efficiency of the maintenance team, identifying areas of improvement, and acknowledging successful outcomes.
-
Identifying Trends: Analyzing data to identify recurring issues, trends, or patterns that may require proactive measures to prevent future problems.
-
Continuous Improvement: Using the insights gained from the analysis to implement growth strategies. This may involve refining processes, adjusting resource allocations, or providing additional training.
The Work Order Management process is cyclical, with the data collected during each phase contributing to the enhancement of future maintenance operations. In the following sections, we will explore specific best practices for optimizing each step of the maintenance process, minimizing equipment downtime.
Top 5 Work Order Management Best Practices
Standardize Work Order Formats

Standardizing work order formats is foundational to effective Work Order Management. By establishing a consistent template, organizations ensure that essential information is captured uniformly across all work orders. This includes details such as task descriptions, required resources, timelines, and designated personnel. Standardization not only enhances clarity but also facilitates easier tracking, analysis, and reporting.
Prioritize and Monitor Work Orders
Prioritization is a key aspect of efficient Work Order process. Organizations should categorize work orders based on urgency, impact on operations, and safety considerations. This allows for the allocation of resources to critical tasks first, minimizing unplanned downtime and preventing potential issues. Regular monitoring of work orders ensures that tasks are progressing according to plan, and adjustments can be made promptly if priorities shift.
Assign Work Orders to the Right Technician
Optimizing workforce allocation is essential for effective Work Order Management. Assigning the right work orders to technicians with the appropriate skills and expertise ensures tasks are executed efficiently. This not only enhances the quality of maintenance but also contributes to the overall productivity of the workforce. Matching the right technician to each task minimizes errors, reduces labor hours, and improves overall job satisfaction.
Continuous Improvement
Ongoing improvement is a fundamental principle for any successful management strategy. Regularly assessing and refining Work Order process ensures they remain aligned with organizational goals and industry best practices. This involves seeking feedback from stakeholders, analyzing performance metrics, and implementing changes to enhance efficiency. Embracing a culture of improvement fosters adaptability and ensures the sustainability of effective Work Order process.
Implement a CMMS Software solution
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a transformative solution for modern Work Order process. CMMS software streamlines the entire process by automating tasks, providing real-time visibility, and generating insightful reports. It centralizes data, assign priorities, allowing for efficient communication among stakeholders and enabling high priority maintenance task completion. Implementing a CMMS solution enhances the accuracy of work orders, reduces manual errors, and contributes to the overall efficiency of maintenance operations.
Incorporating these best practices into your Work Order process can significantly impact operational effectiveness, resource utilization, and the longevity of assets. The synergy of standardized processes, prioritization, skilled workforce allocation, a culture of growth, and advanced CMMS software solution creates a robust framework for success.
Conclusion
An effective Work Order Management is critical for organizations aiming to maintain optimal operational efficiency and asset performance. By following best practices such as standardizing work order formats, prioritizing tasks, assigning work order strategically, fostering a culture of improvement, and leveraging cutting-edge CMMS software solutions, businesses can revolutionize their maintenance processes.
These practices not only enhance communication and resource allocation but also contribute to cost savings and overall productivity. As industries evolve, embracing these proven strategies ensures that organizations not only meet the challenges of today but also lay a resilient foundation for future success in the dynamic landscape of maintenance management.